SCIENCE – University of the Philippines Diliman


FEATURED NEWS
Nagsulong ang mga scientist mula sa University of the Philippines–Diliman College of Science (UPD-CS) ng greener approach sa silver nanoparticle (AgNP) synthesis sa pamamagitan ng paggamit ng gamma irradiation kasama ng natural na seaweed-derived biopolymer ι-carrageenan. Bagaman dati nang naiulat ang mga rutang gamma-radiolytic para sa pagbuo ng AgNP, ang mismong papel ng ι-carrageenan sa pag-stabilize at pag-impluwensya sa pagbuo ng nanoparticle sa ilalim ng proseso ng radiolysis ay nanatiling hindi pa ganap na nauunawaan.
The College of Science Office of the Associate Dean for Academic Affairs (OADAA) invites all newly enrolled graduate students to this semester's New Graduate Student Orientation on March 2, 2026 (Monday) 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM at the CS Admin Building Auditorium.
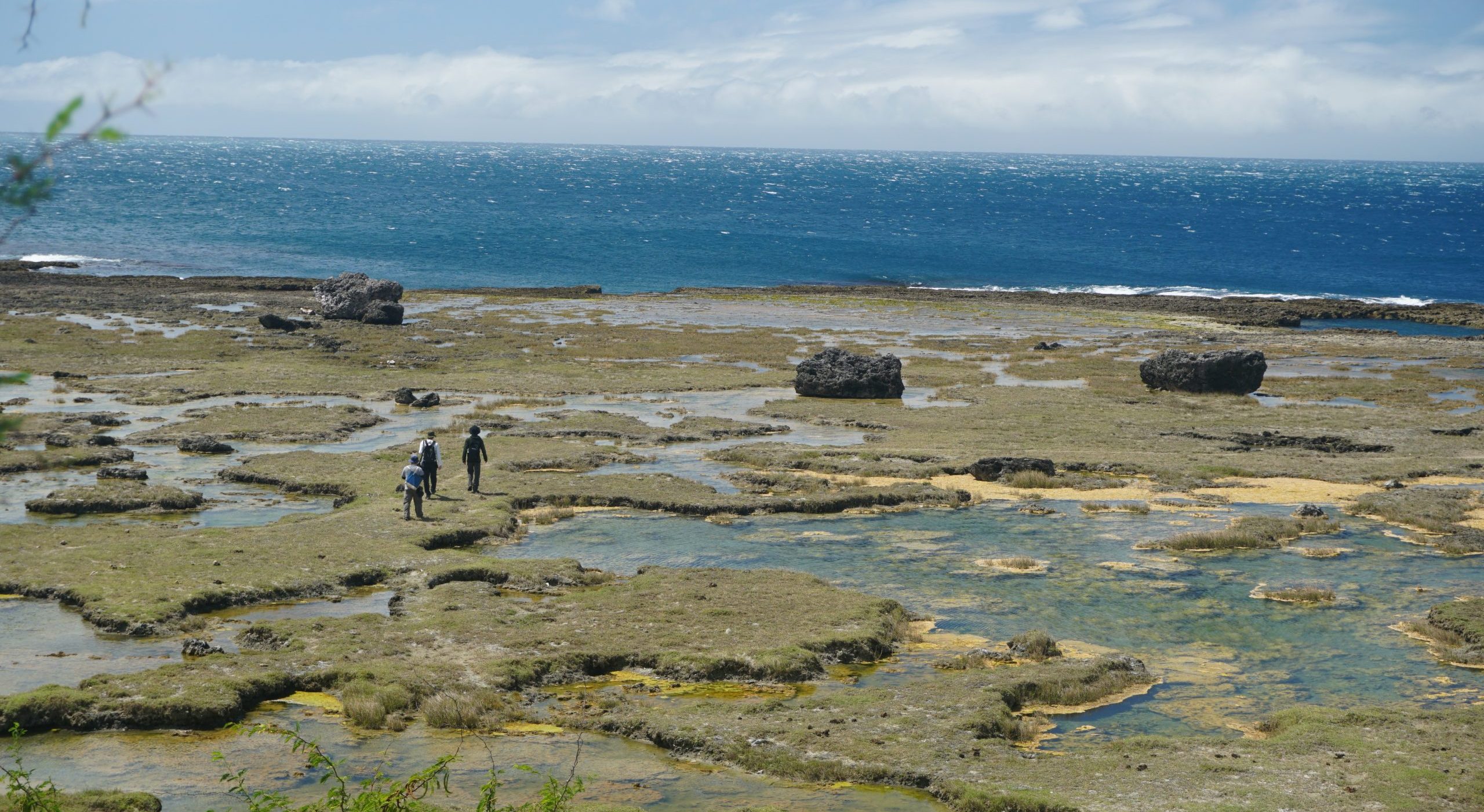
Nakita mo na ba ang mga malalaking tipak ng bato, ang ilan ay kasinglaki ng malaking trak, na nakakalat sa mabatong baybayin ng Pasuquin, Ilocos Norte? Ang mga dambuhalang bato ay makikitang nakapatong sa taas ng nakaangat na reef platform na malayo sa dagat. Pinapaniwalaan na ang mga ito ay bahagi or piraso ng isang sinaunang bahurang koral (ancient coral reef) na napunit at naihagis papaloob ng lupa, dala ng matitinding alon.
Nagsulong ang mga scientist mula sa University of the Philippines–Diliman College of Science (UPD-CS) ng greener approach sa silver nanoparticle (AgNP) synthesis sa pamamagitan ng paggamit ng gamma irradiation kasama ng natural na seaweed-derived biopolymer ι-carrageenan. Bagaman dati nang naiulat ang mga rutang gamma-radiolytic para sa pagbuo ng AgNP, ang mismong papel ng ι-carrageenan sa pag-stabilize at pag-impluwensya sa pagbuo ng nanoparticle sa ilalim ng proseso ng radiolysis ay nanatiling hindi pa ganap na nauunawaan.
The College of Science Office of the Associate Dean for Academic Affairs (OADAA) invites all newly enrolled graduate students to this semester's New Graduate Student Orientation on March 2, 2026 (Monday) 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM at the CS Admin Building Auditorium.
Nakita mo na ba ang mga malalaking tipak ng bato, ang ilan ay kasinglaki ng malaking trak, na nakakalat sa mabatong baybayin ng Pasuquin, Ilocos Norte? Ang mga dambuhalang bato ay makikitang nakapatong sa taas ng nakaangat na reef platform na malayo sa dagat. Pinapaniwalaan na ang mga ito ay bahagi or piraso ng isang sinaunang bahurang koral (ancient coral reef) na napunit at naihagis papaloob ng lupa, dala ng matitinding alon.
CS DRIVE
Database of Researches, Innovations, Ventures, and Extension Projects